
Lead routing is an automated function of Aimbase. When leads enter the platform either from the API or through the file import process, Aimbase references the country codes and zip/postal codes on the leads and uses them to match the lead to the most appropriate dealer based on the brand assignments as well as other factors. Lead routing logic can be determined by several different methods or a combination of those methods.
What are Lead Routing Logic Methods?
Radius: The most basic form of lead routing within Aimbase. Regardless of all other forms of lead routing, radius is always used unless specifically disabled for an instance of Aimbase. When radius is disabled, any leads that fall outside of other lead routing logic methods are assigned to the default dealer.
NOTE: the default lead routing radius is 1,500 miles.
For U.S.,Canada, and international and leads, the most basic method of routing leads to dealers within Aimbase is radius routing. This method involves finding the center point of the zip/postal code provided on the lead and calculating its distance from the precise latitude-longitude of the closest dealer.
By default, radius is available for US and Canada only. The radius routing for international countries must be enabled. For international radius, a dealer must be located within the same country as the lead for the dealer to be assigned the lead. If there isn't a dealer located in the same country as a lead, the lead will be routed to a default dealer.
Territory assignments: Territory assignments are most commonly layered on top of radius lead routing. The ability to assign territories to dealers is available as a core function of Aimbase and can be used with additional lead routing methods.
Aimbase has two methods of routing leads to dealers based upon territory assignments. These assignments allow you to dictate a dealer’s “area of responsibility”. Areas of responsibility can be created by assigning territories to a dealer based upon zip/postal code, county, state/province, or country.
Within Aimbase the assignments are stored on either the ‘Territories’ page or the ‘Brand Territories’ page. The difference between Territories and Brand Territories is how Aimbase treats the assigned area of responsibility if there is more than one brand involved.
Example:
If the dealer John’s Recreation sells the brands Swiftsteer and Offroader and you use the Territories page to assign the state of Missouri to the dealer, then the dealer will receive leads from prospects for both brands within the state if Missouri.
If you utilize the Brand Territories function, then each brand has the opportunity to have an area of responsibility independent of the other brand within the same dealership.
Product assignments: Less frequently utilized, Aimbase allows users to assign specific products to dealers, thus limiting the leads assigned to a dealer based upon the prospect’s product of interest. The product assignment function requires customization to the dealer locator being used on a brand website if/when data is pulled from Aimbase and requires maintenance each time a model year changes over. When using product lead routing, it becomes even more necessary that all leads are sent to Aimbase with a product of interest included with the detail. For these reasons, this feature must be specifically requested to be enabled.
Lead Re-routing: Aimbase has the ability for leads to be re-routed to the next dealer in line if/when the first dealer assigned to the lead does not view the lead. All other lead routing rules that have been established apply when using this feature. When enabled, Aimbase also looks for whichever dealer would be the next best match to the lead based off the lead routing rules. When using this feature, after the lead has been assigned to as many dealers as the OEM has specified, then the lead is assigned to the default dealer.
In order to stop a lead from re-routing to the next dealer, one of two things must happen:
The link in the Lead Emails To lead notification email is clicked, thus rendering the lead as “Viewed”.
The lead details page is accessed from within Aimbase by the user who is assigned to the lead. NOTE: The email address on the user account must match the email address that the Lead Emails To contact type is assigned to for this method to work.
Below are different factors that can be dictated by the OEM when utilizing the Lead Re-routing functionality.
Number of dealers each lead is allowed to be re-routed to before being assigned to the default dealer.
Number of minutes the dealer is allowed to be assigned to the lead without viewing before the lead is reassigned to the next best dealer. This value is calculated in minutes, but this can also be setup to hours, days, weeks, etc. based on criteria set by the OEM.
On which days (if any) leads should not re-route to a different dealer.
When utilizing this configuration, any days being skipped still count toward the maximum number of minutes a dealer is allowed to be assigned to the lead without viewing. This configuration only ensures that, if a lead reaches the maximum number of minutes on a day being skipped, then the reassignment will be delayed until the same time on the next day eligible for lead re-routing.
The lead re-routing function has implications for the standard set of reports in Aimbase, any dealers using CRMs to view their leads, dynamic content in autoresponders and nurture emails, and other optional functions of Aimbase. For these reasons, this feature must be specifically requested to be enabled.
What are General Rules Related to Lead Routing?
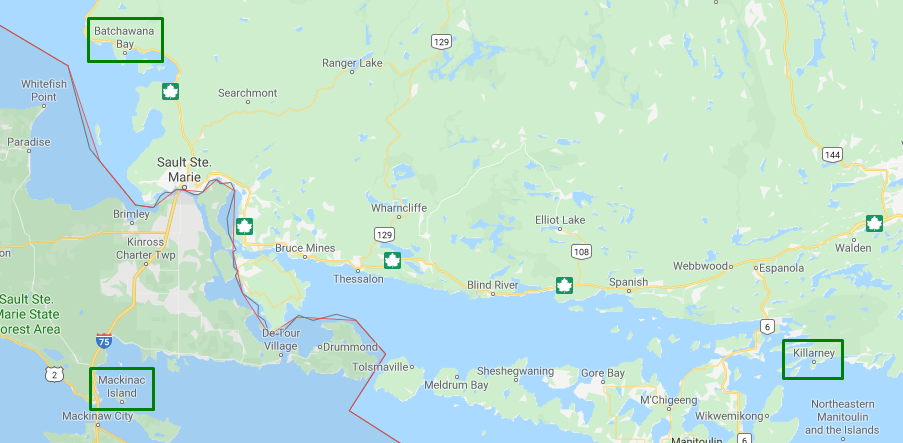
1. Lead routing doesn’t cross country lines. Example: There are dealer locations Mackinac Island, Michigan and Killarney, Ontario. A lead from a customer in Batchawana Bay, Ontario goes through the lead routing process and gets assigned to the dealer in Killarney, Ontario. This happens because even though the dealer in Mackinac Island is closer, it is in a different country.
2. In the U.S., leads routed with the ‘closest dealer’ logic are calculated “as the crow flies”. Example: Dealer A is 15 miles point-to-point from the lead and 25 miles driving distance. Dealer B is 18 miles point-to-point from the lead and 20 miles driving distance. The lead will be assigned to Dealer A even though the driving distance is further, because “as the crow flies” it is the closer dealer to the lead.
3. A prospect’s distance from a dealer is calculated based upon the center point of the zip code associated to the lead. When a lead is created within Aimbase, the system calculates the latitude-longitude of the center point of the postal/zip code provided by the prospect. Once this is determined, Aimbase uses the latitude-longitude from the calculation to determine which dealer is closest based on the latitude-longitude on each ‘Active for Sales’ dealer.
4. When territories are assigned to more than one dealer, the dealer with the assignment who is geographically closest to the zip/postal code on the lead will be assigned to the lead. Zip/postal codes cannot be shared by two dealerships. Most countries outside of the U.S. and Canada cannot be shared by more than one dealer.
What is the Relationship to Dealer Locators?
If you’re using the Aimbase dealer locate API to feed the Find a Dealer feature on your website, the results on this locator will mimic how the lead would be assigned to a dealer in Aimbase. The logic for both is the same and cannot be configured to operate on different sets of rules.
What are Exceptions of Lead Routing Rules?
When leads are sent to Aimbase with the dealer pre-assigned to them, all steps (listed above) normally taken to determine the best dealer for the lead are skipped. Leads enter Aimbase either by file import or API. On these files is a field that allows a lead to be manually assigned to a dealer. This is done simply by passing a dealer number into Aimbase with the rest of the lead information. When this happens, Aimbase skips all other steps related to routing the lead to a dealer and assigns the lead to the dealer included in its details.
Example Scenarios:
Lead is entered by a user from the dealer locator - In some instances, a manufacturer might choose for a consumer to see a “Contact This Dealer” call to action on the results of a dealer search. Often when this feature is available, the website will record the dealer number of the dealer clicked and pass it with the lead information into Aimbase. This ensures that if the consumer provided an address more relevant to the location they need the dealer to be near and then enter a permanent/home address on the form, that the lead will still go to the dealer nearest to where its services are needed.
Historical data or third-party sources - When importing historical data or data that may have been assigned to a dealer in another system or during another process, it is common to insert the data into Aimbase with the pre-existing dealer assignment in-tact.
What are Lead Routing Questions?
In order to locate the information needed to answer your questions about why a lead routed to a dealer the way it did, there are a few key areas of Aimbase you'll want to make sure you can access on the lead details page:
- Lead Staging link/button on the lead details page.
- This will give you direct access to the page where the lead information was staged. From here you can see logging with additional details regarding how/why the lead was assigned to the dealer it was.
- Lead History link/button on the lead details page.
- This is helpful to reference as it holds information about changes that have been made to the lead since it was first staged. If a lead has changed hands from one dealer to another, you can find information about the event(s) here.
- Dealer Match Type
- This can be leveraged as a filter from the leads grid and is also a field on the lead details. This is helpful to provide insight into how lead routing took place most recently for this lead even before digging into the history.
- Territory: Lead fell within dealer’s assigned territory.
- Radius: Dealer is the closest to the lead as calculated by the center point of the lead's postal code. This is an "as the crow flies" calculation.
- Drive Distance: Lead was routed by radius but using a drive distance calculation rather than an "as the crow flies" calculation. (This is an optional feature that requires additional setup.)
- Default: The lead was assigned because the lead either fell outside the assignable dealer territory (white space) or the postal code/country code is invalid..
- Reassigned: The lead was manually assigned to the dealer.
- Pre-assigned: The lead was assigned to dealer upon entry to Aimbase.
- Dealer Group: The lead was assigned to the dealer because it is within a dealer group.
- Inventory: Closest dealer with matching inventory. (This is an optional feature which can only be enabled if the OEM is also running an inventory program.)
- Re-Route: A lead was automatically re-routed to the next closest dealership because the first dealer didn’t acknowledge the lead. (This is an optional feature that is set up with parameters set by OEM.)
- This can be leveraged as a filter from the leads grid and is also a field on the lead details. This is helpful to provide insight into how lead routing took place most recently for this lead even before digging into the history.

- Lead staging section under Imports.
- While you can get to a specific lead’s staging details directly from the lead details, this section of Aimbase is where those details live.

What are Steps to Finding Answers?
- Check the Dealer Match Type to determine if the value in the field addresses your question about lead routing.

2. Check the lead history to for more detail about what may have occurred with the lead's routing.

- Below is an example of one message you may see if something has changed with the lead's dealer assignment at some point. In the screenshot below, you can see where the history tells us that the lead entered Aimbase already assigned to the Testing Dealer. It later underwent a manual reassignment by a user through the system.

3. If nothing is there, use the staging link to get to the staging details.


4. What to look for in the staging log to get the answer.
Example 1: Lead with valid postal code is routed to a dealer based on the dealer being closest to the lead.

Example 2: Lead with invalid postal code is routed to the default dealer (also sometimes referred to as the corporate dealer). In the screenshot below the notable difference between the invalid and valid postal code is the lack of Aimbase appending a county based on the postal code. Because the postal code is invalid, a county cannot be appended. Note the clearly invalid postal code in the customer details to the left.

Example 3: Lead is assigned to a specific dealer that was selected before sending the lead to Aimbase.

FAQs
What is lead routing in Aimbase?
Lead routing in Aimbase is an automated function that assigns incoming leads—via API or file import—to the most appropriate dealer. When a lead enters the system, Aimbase references the country code and the lead’s zip/postal code to calculate a best match to one of the dealers, based on the brand assignments and other configured factors.
Why is lead routing important?
Because correct routing ensures that leads reach the right dealer in a timely manner, which improves conversion chances, avoids mis-assignment, and aligns with brand/dealer responsibilities. It also ensures consistency with how the website’s “Find a Dealer” locator works (if applicable).
What routing methods does Aimbase support?
Aimbase supports several methods (which can be used alone or in combination):
Radius routing: this is the most basic form and always used unless disabled. It calculates the distance between the lead’s postal code center-point and dealer lat/long coordinates.
Territory assignments: dealers can be assigned territories (zip/postal code, county, state/province, or country) to define their “area of responsibility.” Aimbase supports both general Territories and Brand-specific Territories (where each brand can have its own territory assignment within the same dealer).
Product assignments: (optional, less common) leads are assigned to dealers based on a specified product of interest. This requires customization, and leads must include product-of-interest data when sent.
Lead re-routing (automated reassignment): if enabled, leads can be automatically sent to the next best dealer if the first assigned dealer does not view the lead within a configured timeframe. At that point other routing logic continues.
How does radius routing work?
Radius routing calculates the distance between:
- The lead’s postal/zip code center‑point, and
- Each dealer’s exact latitude/longitude coordinates.
Additional notes:
- Default radius = 1,500 miles.
- U.S. and Canada radius routing is enabled by default.
- International radius routing must be explicitly enabled and only considers dealers within the same country.
- If no dealer exists in the lead’s country, the lead is routed to the default dealer.
How do territory assignments differ from radius routing?
Territory assignments define specific geographic responsibility for a dealer (by postal code, county, state/province, or country). When territories are assigned, they are typically layered on top of the radius logic.
Example: a dealer “John’s Recreation” sells brands Swiftsteer and Offroader. If you assign the state of Missouri using the Territories page, then the dealer will get leads for both brands in Missouri. Conversely, if you use the Brand Territories page, then each brand could have different territory assignments even within the same dealership.
What should I know about the product-assignment routing method?
Product assignment is less frequently used and must be explicitly enabled.
It requires that leads include the product of interest. Without that, the routing cannot apply.
It also needs maintenance when model years change, because product listings evolve.
What is lead re-routing, and when is it used?
When enabled, if a lead is assigned to a dealer and the dealer does not view the lead within a predefined timeframe, Aimbase will select the “next best match” dealer (based on the same routing logic) and assign the lead to them. Eventually after the configured number of dealer attempts, the lead may go to a default dealer.
The parameters that can be set by the OEM include:
Number of dealers a lead is allowed to be re-routed to before it goes to the default dealer.
The maximum minutes (or hours/days/weeks) a dealer is allowed the lead without viewing before reassignment.
On which days (if any) re-routing should not occur. Note: skipped days still count toward the allowed minutes time.
Because this function affects standard reports, dealer CRMs, dynamic autoresponders and nurture programs, it must be specifically requested/enabled.
What are the general rules related to routing that apply in Aimbase?
Lead routing doesn’t cross country lines. Example: even if a U.S. dealer is geographically closer than a Canadian dealer, a lead from Ontario will route to the Canadian dealer because country-line is respected.
In the U.S., the “closest dealer” logic uses straight-line (“as the crow flies”) distance, not driving distance. Example: Dealer A is 15 miles straight-line and 25 miles driving; Dealer B is 18 miles straight-line and 20 miles driving. The lead will go to Dealer A.
The distance calculation uses the center point of the lead’s postal/zip code.
When a territory is assigned to more than one dealer, the dealer with the assignment and the closest geographic distance to the lead’s zip/postal wins. Zip/postal codes cannot be shared by two dealerships; in most countries outside the U.S./Canada, dealers cannot share postal codes.
How does the routing logic relate to the “Dealer Locator” on a brand’s website?
If you are using Aimbase’s dealer locate API (for a “Find a Dealer” website feature), the API’s results will mimic the same routing logic that Aimbase uses for lead assignment. The logic is the same and cannot be configured separately.
What are the exceptions to the standard lead-routing rules in Aimbase?
One key exception is when the lead is sent into Aimbase with a dealer pre-assigned. In that case, all the routing logic steps (radius, territory, etc.) are skipped, and the lead goes straight to the specified dealer.
Examples of when this may occur:
A consumer on the website clicks “Contact This Dealer” and the website passes the dealer number with the lead.
Historical data imports or third-party sources where leads already had dealer assignments and are imported with that assignment intact.
How can I check why a particular lead was routed the way it was?
You can examine the following in Aimbase:
The Dealer Match Type field on the lead details page (and filterable in the leads grid). The types include: Territory, Radius, Drive Distance (if enabled), Default (when outside territory or invalid postal), Reassigned, Pre-assigned, Dealer Group, Inventory (optional) or Re-Route.
The Lead History link/button on the lead details page. This shows changes made to the lead since staging (e.g., dealer changes).
-
The Lead Staging link/button on the lead details page (or via Imports > Lead Staging). This shows the staging log and click-through details for how/routing decisions were made.
Steps to investigate:If you still need more detail, open the lead staging log to review the routing log entries.
-
Look for specific signs, for example:
A lead with a valid postal code routed via “Closest Dealer”.
A lead with an invalid postal code assigned to the default dealer (notice no county appended in the log).
A lead that was pre-assigned to a dealer and routing logic was bypassed.
What should I do if a lead was assigned to a dealer but that dealer didn’t view it and I want to understand the impact?
If the lead re-routing functionality is enabled, when a dealer fails to view a lead within the configured timeframe, the system moves the lead to the “next best match” dealer. In those cases, investigate:
Has the “Viewed” link in the lead notification email been clicked? If not, the system counts that as a non-view.
Has the assigned user accessed the lead details page (and does their email match the “Lead Emails To” contact type)? If not, the assignment is treated as “not viewed.”
What are the OEM configured thresholds: number of allowable re-routes, time-window, days to skip?
Because re-routing changes lead ownership, it can have downstream implications for reporting, CRM integrations, email autoresponders, nurture workflows, and dynamic content, so it must be carefully implemented.
What happens if a lead’s postal/zip code is invalid or falls outside assignable territory?
If the postal/zip code cannot resolve (e.g., county cannot be appended) or falls outside the assigned territory radius/territory region, then the lead is assigned to the default dealer (also referred to as the corporate dealer). Example: invalid postal code → no county appended → default dealer.
What are any country-specific nuances I should be aware of for lead routing?
Lead routing does not cross country boundaries. Even if a dealer across the border is closer, the lead stays within the lead’s country.
International radius routing is not enabled by default: an OEM must enable radius routing for international countries, and only dealers within the same country will be considered.
For distance calculations, in the U.S., “straight-line” distance is used unless a “drive distance” feature (optional) is configured.
What is the difference between “Territories” and “Brand Territories”?
“Territories” assign the geographic region to a dealer for all brands the dealer sells. Example: Dealer A sells Brand X and Brand Y; if State Z is assigned via Territories page, Dealer A receives leads for both brands in State Z.
“Brand Territories” allow each brand to have independent geographic assignments even within the same dealership. This means Brand X and Brand Y can have different regions for the same dealer.
What is the “default dealer” in Aimbase?
The default dealer is the dealer to which leads are assigned when none of the routing logic methods match or if leads fall outside configured geography, or if the lead’s country has no dealer (in international cases), or if the dealer fails view and exceeds re-routing thresholds. It acts as a catch-all.
If I’m using a “Find a Dealer” website feature via Aimbase dealer-locate API, do I need a separate routing logic?
No. The dealer-locate API uses the exact same routing logic as Aimbase’s lead-assignment system. The logic cannot be configured differently for the website vs lead assignment.
What fields or tools in Aimbase help support troubleshooting of lead routing?
For investigation you should use:
Dealer Match Type: this indicates how the lead was routed (Territory, Radius, Drive Distance, Default, Reassigned, Pre-assigned, Dealer Group, Inventory, Re-Route).
Lead History: shows changes to the lead’s assignment since staging.
Lead Staging/Lead Staging link: shows the staging log with detailed routing logic and why decisions were made.
What are any other considerations or warnings when using routing logic or enabling advanced features?
A few things to keep in mind:
If re-routing is enabled, it can affect reports, CRM integrations, dynamic content in autoresponders and nurture programs. It must be specifically requested and configured.
Product-based routing requires the leads to include product-of-interest information, and must be maintained each model year. Without that, leads may not route correctly.
Postal/zip code centroids are used for distance calculations, so in border or large-postal-area cases actual driving time may differ from “straight-line” distance. Be aware of this especially if you set strict radius thresholds.
For international countries, enabling radius routing and ensuring dealer country matches lead country are critical. Otherwise leads may stray to default.
Territory overlap: When multiple dealers cover the same territory, the closest dealer wins (by geographic center-point distance). Postal codes cannot be shared in many markets.